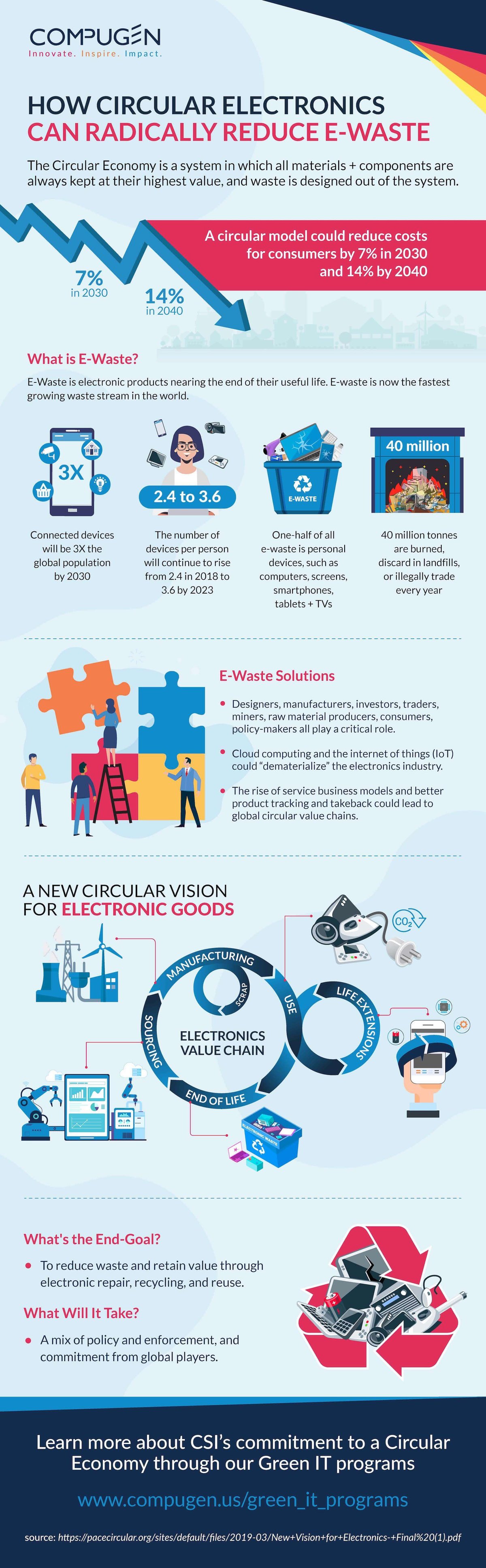
Circular Economy Infographic
Circular electronics, a sustainable approach to electronic product design and lifecycle management, holds the potential to dramatically reduce the environmental impact of electronic waste (e-waste). Unlike the traditional linear model of "take, make, dispose," circular electronics embrace reusability, repairability, and recycling principles to create a closed-loop system that minimizes waste generation and maximizes the lifespan of electronic devices.
Design for Durability and Repairability
Circular Electronics prioritizes designing durable, modular, and easy-to-repair products. This extends the lifespan of electronic devices, reducing the frequency with which consumers need to replace them. Products become more economically and environmentally sustainable over time by making components replaceable, such as batteries and screens.
Reuse and Refurbishment
Circular electronics emphasize the importance of reusing electronic devices. It can be refurbished, upgraded, and resold rather than discarding a product at the end of its first life cycle. This not only extends the product's life but also reduces the demand for new manufacturing, lowering the overall environmental footprint of the electronics industry.
Recycling and Material Recovery
Circular electronics promote responsible recycling practices to extract valuable materials from end-of-life devices. Proper recycling processes recover precious metals, plastics, and other materials, diverting them from landfills and reducing the need for raw material extraction. This approach significantly minimizes environmental degradation associated with mining and extraction processes.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
Circular electronics embrace the concept of extended producer responsibility, where manufacturers are accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products. This encourages companies to design products with recyclability in mind and motivates them to establish take-back programs to manage the disposal of end-of-life products responsibly.
Digital Services and Product-as-a-Service (PaaS) Models
Circular electronics explore innovative business models such as product-as-a-service (PaaS), where consumers lease or subscribe to electronic devices rather than own them outright. This encourages manufacturers to design products for durability and incentivizes them to take back and refurbish devices at the end of the lease period, creating a more sustainable consumption cycle.
.png)